반응형
Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 국비코딩
- 정보처리기사실기정리
- 정보처리기사요약
- ReactNative
- 자바스크립트 코딩테스트
- typescript
- 정보처리기사
- 평일코딩
- 리액트네이티브
- spring
- php
- 이안의평일코딩
- 오라클
- 국비IT
- 코딩테스트
- 정보처리기사정리
- 타입스크립트
- 자바의정석
- react
- Oracle
- 정보처리기사실기
- 자스코테
- CSS
- 리액트
- VUE
- 스프링
- javascript
- 정보처리기사실기요약
- 자바스크립트
- Java의정석
Archives
- Today
- Total
이안의 평일코딩
[PHP] 함수의 활용 (return) 본문
반응형

PHP 함수
return
return이 나오면 함수가 종료되고 나머지 코드는 무시된다.
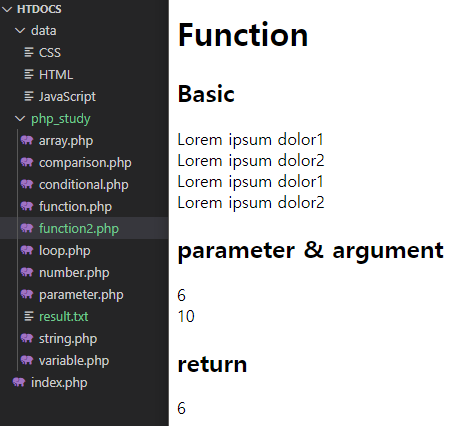
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>function2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Function</h1>
<h2>Basic</h2>
<?php
function basic(){
print("Lorem ipsum dolor1<br>");
print("Lorem ipsum dolor2<br>");
}
basic();
basic();
?>
<h2>parameter & argument</h2>
<?php
function sum($left, $right){
print($left+$right);
print("<br>");
}
sum(2,4);
sum(4,6);
?>
<h2>return</h2>
<?php
function sum2($left, $right){
return $left+$right;
}
print(sum2(2,4));
file_put_contents('result.txt', sum2(2,4));
// sum2()의 결과값이 result.txt 파일에 저장되어 생성된다.
?>
</body>
</html>
함수의 활용
Before
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo $_GET['id'];
} else {
echo "Welcome";
}
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
$list = scandir('./data');
$i = 0;
while($i < count($list)){
if($list[$i] != '.') {
if($list[$i] != '..') {
echo "<li><a href=\"index.php?id=$list[$i]\">$list[$i]</a></li>\n";
}
}
$i = $i + 1;
}
?>
</ol>
<h2>
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo $_GET['id'];
} else {
echo "Welcome";
}
?>
</h2>
<?php
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo file_get_contents("data/".$_GET['id']);
} else {
echo "Hello, PHP!";
}
?>
</body>
</html>위의 코드를 함수를 통해 가독성 있게 바꿔보자.
After
<?php
function print_title(){
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo $_GET['id'];
} else {
echo "Welcome";
}
}
function print_description(){
if(isset($_GET['id'])){
echo file_get_contents("data/".$_GET['id']);
} else {
echo "Hello, PHP!";
}
}
function print_list(){
$list = scandir('./data');
$i = 0;
while($i < count($list)){
if($list[$i] != '.') {
if($list[$i] != '..') {
echo "<li><a href=\"index.php?id=$list[$i]\">$list[$i]</a></li>\n";
}
}
$i = $i + 1;
}
}
?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>
<?php
print_title();
?>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1><a href="index.php">WEB</a></h1>
<ol>
<?php
print_list();
?>
</ol>
<h2>
<?php
print_title();
?>
</h2>
<?php
print_description();
?>
</body>
</html>함수를 이용하면 정리정돈되어 훨씬 가독성이 좋아지며 재사용도 가능해진다.
반응형
'Back-end > PHP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PHP] 리팩토링 (require), XSS, htmlspecialchars, basename (0) | 2021.04.02 |
|---|---|
| [PHP] POST방식과 CRUD (rename, unlink) (0) | 2021.04.02 |
| [PHP] 반복문과 조건문의 활용 (scandir) (0) | 2021.04.02 |
| [PHP] PHP의 기초(2) - 함수, 조건문, 반복문, 배열 (0) | 2021.04.02 |
| [PHP] PHP의 기초(1) - 환경설정, 데이터타입, 변수, 파라미터 (0) | 2021.04.01 |
Comments




